Chapter 4. Getting Online
There are many types of Internet connections including:
ISDN Connection
Modem Connection
xDSL Connection
Cable Modem Connection
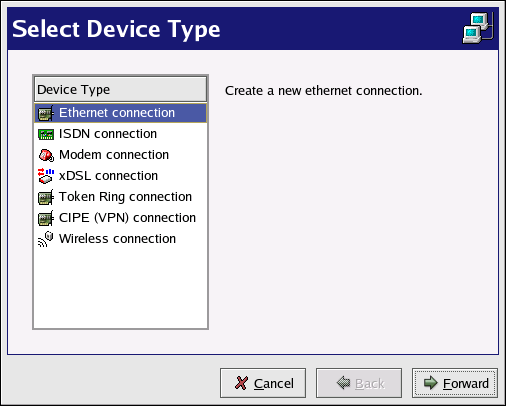
The Internet Druid application can be used to configure an Internet connection in Red Hat Linux.
If you would like to configure an Internet connection in Red Hat Linux, you can use the Internet Druid application.
To use Internet Druid, you must be running the X Window System and have root privileges. To start the application, use one of the following methods:
In the graphical desktop environment, go to the Main Menu => System Tools => Internet Configuration Wizard.
At a shell prompt, type the command internet-druid
In both cases you will have to enter your root password to continue.
Your own ISP may have specific connection requirements for their service which differ from the instructions in this chapter. Before connecting, check with your ISP for any specific instructions that they provide, including the following information:
The phone number that your modem must dial to connect to your ISP if you are using a modem.
Your login name and password for the ISP account.
A gateway address. Some ISPs may require you to configure a gateway address.
DNS entries: DNS means Domain Name System. DNS servers act as a road map for the Internet. When you use the Internet, the DNS tells your machine where to send its message traffic. DNS tracks IP (Internet Protocol) addresses; each computer connected to the Internet must have an IP address, which is a unique set of numbers like 2xx.2xx.2x.2. You may receive one or more DNS entries from your ISP when you sign up.
- ISDN Connection
An ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) connection uses high-speed, high-quality digital telecommunication lines as opposed to an analog modem connection. This special phone line must be installed by a phone company. To configure this type of connection, start Internet Druid, select ISDN Connection, and follow the steps in the wizard.
- Modem Connection
A modem connection uses a modem to establish a connection to the Internet. Digital data is modulated into analog signals and sent over phone lines. To configure this type of connection, start Internet Druid, select Modem Connection, and follow the steps in the wizard.
- xDSL Connection
An xDSL (Digital Subscriber Line) connection uses high-speed transmissions through telephone lines. There are different types of DSL such as ADSL, IDSL, and SDSL. Internet Druid uses the term xDSL to mean all types of DSL connections.
Some DSL providers require you to configure your system to obtain an IP address through DHCP with an Ethernet card. To configure this type of connection, start Internet Druid, select Ethernet Connection, and select DHCP on the Configure Network Settings screen. Some DSL providers require you to configure a PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) connection with an Ethernet card. To configure this type of connection, start Internet Druid, select xDSL Connection, and follow the steps in the wizard. If you must supply a username and password to connect, you are probably using PPPoE. Ask your DSL provider which method you should use.
- Cable Modem Connection
A cable modem connection uses the same coaxial cable that your TV cable travels on to transmit data. Most cable Internet providers require you to install an Ethernet card in your computer that connects to the cable modem. Then, the cable modem connects to the coaxial cable. The Ethernet card is usually required to be configured for DHCP. To configure this type of connection, start Internet Druid, select Ethernet Connection, and select DHCP on the Configure Network Settings screen.
- Wireless Connection
If you are connecting your Red Hat Linux computer to a wireless access point (WAP) or peer-to-peer (also called ad-hoc) network with a wireless (802.11x) network card, then you will need to configure your wireless device. Choose the Wireless Connection, then select the device from the list provided. You can then configure the device for DHCP or fixed IP addresses In the pop-up device configuration window.
For more detailed instructions, refer to the Network Configuration chapter in the Official Red Hat Linux Customization Guide.